Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC)
Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) are financial institutions that offer financial services like banks without a banking license. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) regulates NBFCs.
What is NBFC?
A Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC) is a company that is registered under the Companies Act, 1956 and is involved in the lending business, hire-purchase, leasing, insurance business, receiving deposits in some cases, chit funds, stocks, and shares acquisition, etc.
The functions of the NBFCs are managed by both the Ministry of Corporate Affairs and the Reserve Bank of India.
Examples of NBFC in India
Some of the examples of Non-Banking Financial Company in India that offer investment options, loans, fund transfer services, leasing, and hire-purchase options are Bajaj Finserv, Power Finance Corporation Limited, Mahindra & Mahindra Financial Service, Shriram Transport Finance Company, Muthoot Finance Ltd, etc.
Different Types of NBFCs
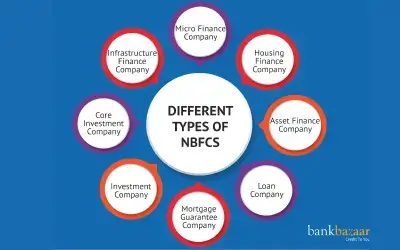
- Asset Finance Company (AFC): An Asset Finance Company primarily provides finance for purchasing physical assets such as machinery, vehicles, and equipment.
- Example: Vehicle loan providers and equipment financing NBFCs.
- Key Role: Supports businesses in expanding their operations by financing capital assets.
- Investment Company (IC): An Investment Company deals with the acquisition of securities such as shares, bonds, and debentures.
- Key Role: Helps in managing investments and creating diversified portfolios for clients.
- Loan Company (LC):A Loan Company provides personal loans, business loans, and other credit facilities to individuals and organizations without involving asset financing.
- Key Role: Offers financial assistance for working capital, expansion, or personal needs.
- Infrastructure Finance Company (IFC): An Infrastructure Finance Company focuses on financing infrastructure projects such as roads, power, telecom, and ports.
- Key Role: Plays a vital role in India’s economic development by funding large-scale infrastructure initiatives.
- Systemically Important Core Investment Company (CIC-ND-SI): These NBFCs hold shares and securities of their group companies but do not trade or deal in them.
- Key Role: Acts as a holding company managing investments within a corporate group.
- Infrastructure Debt Fund – NBFC (IDF-NBFC): An IDF-NBFC facilitates the flow of long-term debt into infrastructure projects by refinancing existing loans.
- Key Role: Supports sustainable infrastructure financing through bonds and debt instruments.
- Micro Finance Institution (NBFC-MFI): A Micro Finance Institution provides small loans to low-income individuals or groups, often without collateral.
- Key Role: Promotes financial inclusion in rural and semi-urban areas.
- Housing Finance Company (HFC): Although governed separately under the National Housing Bank (NHB), HFCs are similar to NBFCs as they provide loans for home purchases, construction, and renovation.
- Key Role: Enables affordable housing access across income groups.
- Mortgage Guarantee Company (MGC): A Mortgage Guarantee Company offers guarantees to lending institutions for housing loans extended to borrowers.
- Key Role: Reduces credit risk for lenders and supports housing finance growth.
- NBFC – Factors: These NBFCs specialize in factoring services, i.e., managing and financing receivables of businesses.
- Key Role: Improves cash flow for companies by converting invoices into immediate funds.
- NBFC – Non-Operative Financial Holding Company (NOFHC): This category acts as a holding company for promoting new banks or financial institutions under RBI’s guidelines.
- Key Role: Helps in maintaining transparency and separation between different financial entities.
Eligibility Criteria to Obtain NBFC License
The fundamental requirements which are to be fulfilled in order to apply for NBFC license are as follows:
- The company has to be registered under the Companies Act. That is the company should either be a Limited Company or a Private Limited Company (PLC).
- The minimum Net Owned Fund of the company must be Rs.2 crore.
Functions and Services of NBFCs
The services offered by NBFCs are:
- Personal Loans
- Vehicle Loans
- Home Loans
- Gold Loans
- Credit Card services
- Microfinance
- Insurance Services
- Services related to leasing and hire purchase
- Services related to investment and asset management.
Features of NBFCs
The main features of NBFCs are mentioned below:
- Specific sectors such as small businesses, microfinance, and infrastructure are often catered by NBFCs.
- NBFCs offer factoring, leasing, wealth management, retirement planning, and credit facilities services other than lending.
- RBI regulates NBFCs.
- Demand drafts cannot be accepted by NBFCs.
Benefits of NBFCs (Non-Banking Financial Companies)
Below are the key benefits that make NBFCs a preferred choice for borrowers and investors alike:
🔹 Faster Loan Approvals: NBF's use technology-driven credit assessments, making it easier for individuals and small businesses to access funds quickly.
🔹 Easy Access to Credit: NBFCs serve customer segments often overlooked by traditional banks, such as small business owners, startups, and borrowers in rural areas.
🔹 Simple Documentation: Compared to banks, NBFCs have minimal documentation and simpler procedures.
🔹 Wide Range of Services: NBFCs offer a diverse portfolio of financial products, such as: Personal and business loans, Vehicle and gold loans, Microfinance services, Investment and wealth management products.
🔹 Competitive Interest Rates: NBFCs provide loans at competitive or customized interest rates
🔹 Technology-Driven Services: Leverage digital platforms for loan applications, EMI tracking, and online repayments.
🔹 Support for Financial Inclusion: NBFCs bridge the gap between formal banking and unbanked populations, empowering individuals in rural and low-income segments.
🔹 Attractive Investment Options: Investors can benefit from NBFC fixed deposits and bonds that offer higher returns than conventional bank FDs, with the added advantage of flexible tenures.
🔹 Regulatory Oversight by RBI: NBFCs operate under RBI guidelines, ensuring financial discipline and protecting customer interests, while maintaining the flexibility to innovate and adapt to market needs.
Difference between NBFC's and Banks
While NBFCs engage in lending and investment activities akin to banks, several notable distinctions set them apart:
Feature | Banks | NBFCs |
Regulatory Authority | Regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) | Regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) |
Acceptance of Deposits | Can accept demand deposits | Cannot accept demand deposits |
Issuance of Cheques | Can issue cheques drawn on itself | Cannot issue cheques drawn on itself |
Deposit Insurance | Available and allowed | NA |
Participation in Payment and Settlement System | Forms part of the payment and settlement system | Does not form part of the payment and settlement system |
Significance | A bank is given the license by RBI to provide banking services to its customers | An NBFC does not possess the banking license from RBI, However, they can provide banking services under the administration and control of the RBI. |
Applicable Act | Banking Regulation Act 1949 | Companies Act 2003 |
License | Banking license provided by RBI | Does not hold a banking license but Certificate of Registration by the RBI |
FDI | Only 74% allowed | 100% FDI is allowed |
Credit Score Requirements | Higher | Moderate to lower credit score can be considered. |
Rules and Regulations | Strict adherence to the rules | Rules and regulations are flexible and suited to the needs of the customer. |
Regulatory Framework for NBFCs in India

Certain entities are involved in the business of financial activities but do not require obtaining a registration with the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). As these entities are regulated by other financial sector regulators, they do not need either the NBFC registration or the NBFC regulations of RBI.
These entities are as follows:
- Insurance Companies which are regulated by Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDA)
- Housing Finance Companies which are regulated by the National Housing Bank
- Stock Broking Companies which are regulated by Securities and Exchange Board of India
- Merchant Banking Companies which are regulated by Securities and Exchange Board of India
- Mutual Funds which are regulated by Securities and Exchange Board of India
- Venture Capital Companies which are regulated by Securities and Exchange Board of India
- Companies that run Collective Investment Schemes which are regulated by Securities and Exchange Board of India
- Chit Fund Companies which are regulated by the respective State Governments
- Nidhi Companies which are regulated by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA)
Incorporation Process of an NBFC
The process of incorporating a Non-Banking Financial Corporation (NBFC) is discussed below:
- The company should have a valid registration under the Companies Act, 1956 or the Companies Act, 2013.
- The company should have a minimum net owned funds worth Rs.2 crore.
- At least one of the Directors has to be of the same background or has to be a Senior Banker. This Director also has to be a full-time director in the company.
- The company should have a clean CIBIL record.
- Once the conditions which are mentioned above are met, the applicant can apply for the incorporation through the website of the Reserve Bank of India.
- An online application has to be filled up and submitted through the RBI website.
- Along with the form, the applicant is required to upload the requisite documents on the online portal.
- Once all of the above-mentioned steps are completed, a CARN number will be generated.
- The applicant is also required to send a hard copy of the application which is filled up and submitted on the portal, to a regional branch office of the Reserve Bank of India.
- The license will be issued to the company, after the thorough scrutinisation of the application.
FAQs on NBFC
- How many NBFCs are there in India?
Registered NBFCs with the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) are nearly 10,000, out of which 89 are deposit-accepting NBFCs.
- What is Net Owned Fund?
Net Owned Fund of a company can be defined as the funds owned by a company after deducting the intangible assets and reserves from its Total Owned Fund.
- What are the four layers of NBFCs?
The four layers of NBFC are Base layer (NBFC – Base Layer (NBFC-BL)), Middle layer (NBFC – Middle Layer (NBFC-ML)), Upper layer (NBFC – Upper Layer (NBFC-UL)), and top layer (NBFC – Top Layer (NBFC-TL)).
- Which is the largest NBFC in India?
Bajaj Finance Ltd. is the largest NBFC in India. It is a deposit-taking NBFC registered with the RBI and reported revenue of ₹22,413 crore.
- Which is the safest NBFC?
Some top-rated NBFCs known for safety and high interest on fixed deposits include PNB Housing Finance, Bajaj Finance, Mahindra & Mahindra Financial Services, and Shriram Finance.
- Who funds NBFC?
Business funds for NBFCs come from short- and long-term loans, Foreign Direct Investment, Bonds, and securitisation of loans.
- How is an NBFC different from a bank?
NBFCs do not accept demand deposits and allow up to 100% foreign investment, unlike banks, which accept demand deposits and are part of the payment system.
- Who is controlling NBFC in India?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) controls the NBFCs in India within the framework of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 (Chapter III-B).
- What is the asset size of NBFCs?
As of March 2022, the total asset size of NBFCs in India is over ₹54 lakh crore. NBFCs with assets over ₹500 crore are considered significant.
- Is Paytm an NBFC?
No, Paytm is not an NBFC. However, it operates financial services through subsidiaries that may be classified under financial institutions.
- Is LIC an NBFC?
No, LIC (Life Insurance Corporation of India) is an insurance company, not categorized as an NBFC.
- Is NBFC a private company?
No, all NBFCs in India are not private companies. They are only registered as public or private limited companies.
- Is an NBFC a private bank?
No, an NBFC is not a bank. It offers certain banking-like services without a banking license and typically doesn’t provide demand deposit facilities.
- Is NBFC governed by RBI?
Yes, all NBFCs are governed by the Reserve Bank of India under Section 45-IA of the RBI Act, 1934, if they hold or accept public deposits.
- Can NBFCs give loans?
Yes, personal loans are given by NBFCs to the borrowers.

Disclaimer
Credit Card:
Credit Score:
Personal Loan:
Home Loan:
Fixed Deposit:
Copyright © 2026 BankBazaar.com.
